
Fats and omega 3

Department of Health guidelines state that we should all eat at least two portions of fish every week, and one of those portions should be oily fish, such as salmon or mackerel.
Surveys show that most people currently only eat one third of a portion of oil-rich fish per week and are therefore falling short of the recommended intake and the associated health benefits of omega 3 fats.
What are fatty acids?
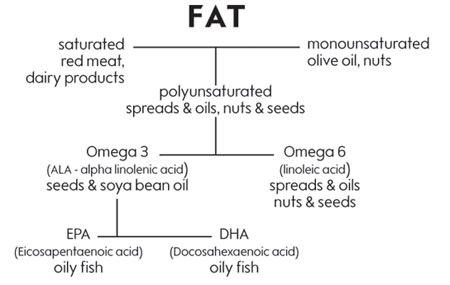
Fatty acids are the building blocks of fat and there are three different types: saturated fatty acids, monounsaturated fatty acids and polyunsaturated fatty acids.
While monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats can lower blood cholesterol and help reduce the risk of heart disease, saturated fats can raise blood cholesterol and increase the risk of heart disease.
There is a special sub group of polyunsaturated fatty acids known as Essential Fatty Acids (EFAs). They are called 'essential' as they are not easily manufactured by the body and must be provided by food. They are split into two groups:
Omega 3 These are found in oily fish, fish oils, some vegetable oils and some nuts and seeds. Omega 3 fats occur naturally in seeds as alpha linolenic acid (ALA), whilst the most effective omega 3 fats occur naturally in oily fish as eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA).
Good sources of ALA include: linseed (flaxseed) oil, linseeds, soya bean oil, pumpkin seeds, walnut oil, rapeseed oil and soya beans.
The body can convert ALA into EPA and DHA, but not very efficiently. This is why oily fish plays such an important role in our diet. Oily fish contains EPA and DHA in a 'ready made' form that the body can use easily.
Omega 6 These are found in vegetable oils, nuts, seeds and grains. In general we get sufficient omega 6 fats in our diet from vegetable oils used in cooking, polyunsaturated spreads, nuts, seeds and grains.
Why are omega 3 fats so important?
Omega 3 fats play an important role in maintaining heart health, as well as helping to maintain healthy cholesterol levels. They also help maintain brain function and vision.
Maternal omega 3 plays an important role in brain and eye development of the foetus and breastfed infants. Mothers-to-be should ensure they have an adequate intake of omega 3 but should not exceed 2 portions of oily fish a week. For more information on diet in pregnancy, click here.
What are the sources of omega 3?
| Food source omega 3 | (g per 100g) |
| Salmon | 2.3 |
| Trout | 1.2 |
| Herring | 2.0 |
| Mackerel | 2.0 |
| Sardines | 2.2 |
| Pilchards | 2.2 |
| Tuna | 1.6 |
| Crab | 1.2 |
| Cod liver oil | 20.0 |
| Linseed (flaxseed) oil | 50.0 |
| Linseeds | 20.3 |
| Pumpkin seeds | 3.5 |
| Soya bean oil | 7.3 |
| Walnut oil | 11.5 |
| Rapeseed oil | 9.6 |
| Soya beans | 1.2 |
| Hemp seed oil | 2.0 |
What about vegetarians and vegans?
If you follow either a vegetarian or a vegan diet, your main dietary source of omega 3 will be from ALA (alpha linolenic acid). As the conversion of ALA in the body to EPA and DHA is not always efficient, it is important to eat lots of plant sources of ALA. Try snacking on walnuts and linseeds, or sprinkling pumpkin seeds on your porridge. Or have you tried dressing your salad with walnut oil.
